
 Home page: Matter is made of waves.
Home page: Matter is made of waves.THE BLOG (2009)
The blog The blog 2008 The blog 2007

 Home page: Matter is made of waves.
Home page: Matter is made of waves.
Please note that I may be too busy to respond to your many messages.
Gabriel LaFreniere Notice. webmaster@glafreniere.com
|
December 31, 2009. Below are two videos which should end sterile discussions on the twin paradox as well as on the train and tunnel paradox. Now, one may rely on the "Alpha" conciliator. From his point of view, the twins are getting older equally. Similarly, the train and the tunnel length is equal. Relativity being what it is, the absolute truth will remain unknown forever, though. The transformations were obtained thanks to my Time Scanner. This device is capable of performing the Lorentz transformations. The videos show that twins A and B obtain perfectly symmetrical results. Although the twin A is truly stationary with respect to the aether, he cannot argue that his point of view is better because the twin B is recording exactly the same situation as he does. It should be pointed out that this is consistent with Lorentz's Relativity, which is possible because the aether exists. As a matter of fact, Relativity becomes totally unexplainable in the absence of the aether. One may easily check that the contraction according to a .866 factor and the 5 second time shift is transferred from A to B. Below is an image of the amazing symmetrical results.
The Lorentz transformations. Left: the twin A and his witness A' whose distance is 10 light-seconds are both stationary with respect to the aether. The twins B and B' , whose beta speed is .5 c, are contracted according to a factor g = Sqr(1 – beta ^ 2) = .866. The B and B' clocks exhibit a 5 slow second time shift according to: –beta * x, with x = 10 and x' = 8.66 light-seconds for B. Right: the twins B et B' are not transformed any more and they observe that A and A' are undergoing the transformations instead. The second video also shows that the waves emitted by A are apparently undergoing the Doppler effect, but it is just an illusion.
The Alpha conciliator (or observer) cannot see any difference between twins A and B. They just seem to move away from him at the same intermediate alpha speed, whose value is derived from Poincare's law of speed addition: alpha = (1 – g) / beta As a result, from the Alpha point of view, their contraction is the same and their clocks are ticking at the same rate of time. Therefore, the three of them are more likely to adopt the same space and time units, even though they are definitely arbitrary, as a convention. There is no need to invoke an absurd and useless space-time transformation any more. Moreover, the transformation difference becomes much less severe. For example, the Lorentz contraction factor is only .9634 instead of .866 using alpha = .268 instead of beta = .5. It becomes obvious that, if they had previously departed simultaneously from the Alpha observer, those A and B twins should return home without any age difference between them, albeit they both should now be a bit younger than Alpha. This occurs because they must travel a longer absolute distance to perform the go and return trip, whatever the Alpha absolute speed is. A possible time effect may occur because of the deceleration and acceleration, but it is immaterial. It would be the same for A and B, it would be less severe because of the slower alpha speed and finally, its relative importance would become negligible if the round trip duration was very long. Thus, invoking a change in the inertial frame of reference is not relevant any more. The train and tunnel paradox is subject to the same conclusions. If the Alpha observer considers that the train and the tunnel share the same length, it becomes pointless for A or B to argue that one of them only may be right. Actually, it will remain unknown forever. This is definitely a blind alley and hence, the Alpha compromise appears preferable. The point is that the Alpha position is the best one. For example, protons are traveling in opposite directions at nearly the speed of light inside the Large Hadron Collider. The collider itself is obviously the best place in order to observe the collisions. Otherwise, as seen from a moving proton, the other protons which are theoretically moving in the opposite direction are "only" moving at nearly the speed of light, and so is the collider, whose speed appears to be just slightly slower. This doesn't make any sense because the actual proton relative speed should be nearly twice the speed of light. October 28, 2009. I finally realized that scientists should proceed to the analysis of two new sciences: Motion Mechanics and Motion Optics. It should be pointed out that Poincare and Einstein were both working on Relativity but that they were especially concerned about "The Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies". As a matter of fact, the Lorentz transformations will lead us well beyond Relativity because they explain the causes, which are far more important than the effects. In short, the Lorentz transformations are nothing else and nothing more than a Doppler effect. Relativity holds true and hence, one should be aware that matter transforms because it is made of waves. This explains Matter Mechanics and especially Newton's laws, for example action and reaction effects where the Doppler effect is obviously involved. This is why this science should be called Motion Mechanics. In addition, studying waves in the presence of motion leads to an important section of Motion Mechanics which should be called Motion Optics. All this was not very clear for Poincare and Einstein and they definitely ended up being confused. Nowadays, though, we have developed new methods and new tools which are capable of doing miracles. 1 – Today's computers are amazingly fast and efficient. I could check Lorentz's equations thouroughfully and I finally realized that Lorentz did not put them down correctly. They were actually created in 1887 by Woldemar Voigt in order to produce an artificial space-time transformation, and Lorentz was well aware that they were inverted. He explained that it was only a "mathematical artifice". After many years of analysis and intense reflection, I finally proposed the reversed version below, which is definitely more correct:
2 – The Delmotte-Marcotte virtual medium is the perfect tool in order to study waves, especially in a moving frame of reference. It is the best one for studying Motion Optics. The waves in the animation below were produced thanks to this remarkable invention. 3 – The Time Scanner, which I invented in March 2004, works much better than Lorentz's equations. Here is an example:
The Time Scanner is the best way to perform the Lorentz transformations. The scanning process produces a Doppler effect, but it may also cancel it. Additionally, Lorentz's contraction and time shift are obvious. Thanks to the Alpha speed, which I discovered only in 2009, the print speed now equals the scan speed.
August 28, 2009. The page on Lorentzian Relativity was upgraded. I added the animated diagram below and two other ones showing the progression of Lorentz's x' and t' variables in a moving system (especially B and B') whose velocity is half of the speed of light. It is a must-read for anyone interested in Relativity.
The goal is to understand why observer B is fooled by those transformations. He is unable to measure his speed through the aether, he feels perfectly at rest and he observes that A is rather moving towards the left even though he is actually at rest. It is all about Lorentz's Relativity, the genuine Relativity theory which pas proposed by Lorentz in 1904. Now, everyone interested in Relativity can easily understand it because I finally succeeded in simplifying it to a surprisingly low level. The formulas are there, you may check them, but the results are already displayed so that it becomes much simpler to understand why none of all those observers A, B or C can tell for sure whether they are moving or not. August 2009. Please examine this small video which I very proud of. It is frankly amazing. It contains a lot of information showing that Lorentz's version of Relativity (1904) was correct. It is a high definition (1280 x 720) Mpeg-4 video using the now well accepted H-264 standard (Divx-7 .mkv Matroska file). I suggest VLC Media Player and the whole bunch of CCCP codecs (not USSR!) which also includes a free version of Zoom Player, which is also excellent. Below is the FreeBasic program which produced the images. The only change that I had to make is the way the Lorentz Transformations must be considered. It should be remembered that they had been borrowed from Woldemar Voigt's equations (1887), which were intended to neutralize the Doppler effect in a moving frame of reference. Not to produce it. Because of this, Lorentz and his friend Poincare used the equation set the same way. It is a well known fact that they considered a moving electron, so that the x' and t' variables were applied to the stationary electron. Very few people pointed out that x' and t' should rather stand for the moving electron variables. Quite reasonably, the x and t variables should apply to the stationary electron. That is why I had to reverse Lorentz's equations this way: x' = g x + b t x = g x' – b t' t' = g t – b x t = g t' + b x' y' = y z' = z Beta normalized speed: b = v / c Contraction
factor: g
= Sqr(1 –
b ^ 2) This equation set (actually a "group", which was a new mathematical concept in 1904) is the reversal of Poincare's symmetric equations. Although these additional equations were absent from Lorentz's 1904 work, he admitted that they did make sense. Lorentz's goal was to show that the Michelson interferometer was undergoing a contraction and that Maxwell's equations were becoming invariant under his transformations. Poincare added the symmetric equation set in order to introduce - also in 1904 - his famous "Relativity Postulate". The important point is that the full equation group shown above is the reversed mirror image of Poincare's. They definitely are not the same. Here, x and t stand for the stationary frame of reference coordinates. The consequences are enormous. Instead of transforming space and time (Lorentz wrote that it was only a mathematical artifice), they rather indicate a contraction (according to g x) and a translation motion (according to b t, which is merely the Galilean transformation, or Galileo's Relativity Principle) of a material system, empty in-between distances included. They also indicate that moving clocks display slower seconds (according to g t) together with a time shift (according to – b x). Thus, my version of Lorentz equations is much more understandable. To put it shortly, these new transformations really indicate what Lorentz had in mind in 1904. I strongly recommend that you verify that I am really making use of this new equation set in the program in order to produce (non correct) the Doppler effect on the right side of the image. This is a flawless demonstration that Voigt's goal was to deal with the Doppler effect, not with space and time. But surprisingly, I also use them to contract B and C, which are observers traveling along with hypothetic material bodies. Their speed is 50% of the speed of light, hence beta = .5 c, but B is moving backward. I use them to slow down the emitters frequency along with the seconds displayed by B and C clocks. And finally, I use them to obtain the time shift with respect to B' or C', whose distance to their twin B or C is 10 light-seconds. It is quite easy to understand that, because the relative speed of a radio signal is faster backward (according to 1 + b = 1.5 c) then forward (according to 1 – b = 0.5 c), B' or C' should indeed exhibit such a time shift as compared to B or C after a clock synchronization procedure using radio signals. Lorentz was fully aware of this anomaly. My Time Scanner is capable of accelerating the whole system where emitters and material bodies are moving at different speeds, on condition that they are already transformed. Here, it is accelerated to 50% of the speed of light to the right. However, C and C' are already moving to the right at this speed, so that their new speed should be the speed of light. But Lorentz and Poincare discovered that no material body is capable of reaching the speed of light. This is why their resulting speed is only .8 c, according to Poincare's law of speed addition which is given by: beta'' = (beta + beta') / (1 + beta * beta') In my opinion, such a magnificent harmony should leave nobody unfeeling. Now, thanks to Lorentz, Relativity can be explained. There are no paradoxes any more. All is clear and logic. On the one hand, it now becomes possible to display more than two material bodies (hundreds, actually) whose speed and direction differ. The results remain perfectly coherent after the scanning process, or the acceleration if you prefer. On the other hand, a preferred stationary frame of reference may be designated as a convention. It should allow all observers to have a better image of their situation. Ideally, it is the one whose speed is intermediate, for instance the red scale as seen from A and B. Surprisingly, this red scale does not transform because its intermediate speed (not exactly .25 c because of Poincare's law of speed addition) is simply inverted after undergoing the acceleration. Its speed being the same, its contraction remains the same, so that A and B can adjust its length when they meet (they must consider that they are moving in opposite directions at the same speed). They can also adjust its clock rate so that it stubbornly displays the "absolute" time on condition that is is placed where x = 0 when A and B meet and on condition that they synchronize all clocks according to t = 0 when they meet, too. The time shift is inverted everywhere else because the red scale is stopped, then accelerated at the same speed in the opposite direction. All becomes perfectly clear. The red scale length does not change and the clock displays the absolute time on condition that A and B, A and C, or B and C (two of them only) designate an intermediate one as a preferred Cartesian frame of reference. Thus, there exists a situation in which space and time remains constant. To put it even clearer, as Euclid, Galileo, Descartes and Newton always thought, space and time do not transform. For instance, an intermediate Cartesian frame of reference may be that of the physicist who is observing two electrons colliding when they are moving in opposite directions at nearly the speed of light. In this case, the electrons relative speed is nearly two times that of the light. According to Lorentz, another observer moving along with one of those electrons would rather see the other electron approaching only at nearly the speed of light. This point of view appears frankly distorted, so that the frame of reference of the collider is much more acceptable. Similarly, let's suppose that a GPS system uses two satellites orbiting in opposite directions (avoiding collisions, though!). Then the observer on earth appears to be the only one capable of correctly analyzing the situation. He observes that the satellites slightly contract and that initially, they indicate a slightly slower time and exhibit a time shift. So he must imperatively impose his own time units to the satellites. There is no Relativity to consider here. What's more, because the GPS system uses many satellites orbiting in the same direction, they cannot be synchronized using radio signals from one to another because of the Sagnac effect (the time shift, actually), although it remains possible to correct the anomaly. It appears preferable to correct the error using radio signals emitted from earth. I also suggest that the center of inertia of the whole solar system should determine the preferred frame of reference in order to verify Mercury's orbit. Only this point may be reasonably postulated to be stationary, so that the speed of Mercury and its orbit does not appear the same as seen from it. In addition, the sun itself rotates around this center of inertia, so that Mercury's orbit is severely modified especially when Jupiter is coming in conjunction with Saturn. Although this is not really a Relativity problem because there is no relativistic speed involved here, the choice of a preferred frame of reference still leads to a better picture of the situation. In practice, Einstein's theory of Relativity appears inapplicable. Establishing a preferred frame of reference is advantageous. The present demonstration indicates that many of them are possible but that some of them are much better. Only Lorentz's version of Relativity allows such a choice. It should be pointed out that all this cannot be explained without the presence of the aether. Even if it cannot be detected, all happens as if it exists because the speed of light must imperatively be related to it. The Lorentz transformations indicate that all this happens solely because of the Doppler effect. This strongly suggests that matter is undergoing the Doppler effect. Matter behaves like waves do. Lorentz's Relativity indicates that matter consists of waves propagating at the speed of light. Such waves need a medium, the aether, so that finally, there is nothing else but the aether... It turns out that the Lorentz transformations are leading us well beyond Relativity. Now, we are dealing with matter mechanics, more exactly the Wave Mechanics. The conclusion is that Newton's laws and that all physical phenomena must be reviewed in order to match the Wave Mechanics.
April 29, 2009. I wrote a program showing that Maxwell's equations cannot become invariant under the Lorentz transformations the way they were released in 1904. Lorentz's theory remains correct, however, on condition that his equations indicate matter transformation, not space and time. This is easily feasible by swapping x and x' variables, and also t and t'. This may appear hard to believe. Yet one must admit that correctly applying the Lorentz transformations to Maxwell's equations is a rather complicated procedure. Those equations were quite new at that time and I suppose that very few experts in radio electricity did examine Lorentz's hypothesis. Most of them may not have well understood Lorentz's or Poincare's procedure either. It appears quite possible that the remaining very few people who detected the anomaly did not dare to challenge Lorentz and Poincare because they were two well known scientists. Surely, x' = g x leads to x = x' / g. Such a perfectly reversible equation set is quite easy to obtain, a lot of them can make Maxwell's equations becoming invariant, but here the goal is to match the very special Doppler effect which was proposed by Lorentz. A slower "time" leads to a slower frequency and the resulting overall longer wavelength finally cancels the normal Doppler transverse contraction, which is the very first condition for Relativity to be true. From this point of view, Lorentz's original equation set leads to a serious anomaly... Additionally, Maxwell's equations are definitely not important here. The goal is to obtain the equation set which produces Lorentz's special Doppler effect involving a slower frequency. Then it becomes easier (and still unnecessary) to check the resulting invariance using Maxwell's equations. The important point is that no wavelength contraction occurs any more on transverse axes: y' = y; z' = z. On a standing wave basis, this also leads to a stunning axial wavelength contraction (and ultimately to matter contraction) according to Lorentz's contraction factor: g = sqr(1 – (v / c) ^ 2). Lorentz's equations were intended to cancel those effects, more exactly to cancel this very special Doppler effect. But they didn't. So I wrote a program (see below) in order to show that the following formula does achieve this: x = g * x' – beta * t' From a mathematical point of view, quite reasonably, the x' variable must be recovered this way: x' = (x + beta * t') / g Then Lorentz's equation becomes recognizable after conversion to the MKS system: x' = (x + v t') / sqr(1 – (v / c) ^ 2) It turns out that there is a serious error here. The t' variable instead of t and the plus sign are required. The time equation must also be corrected this way. However, this is not really a problem on condition that x and x' are exchanged. Surprisingly, swapping x and x' fully restores the correct situation. Instead of dealing with an absurd space transformation, it appears simpler to do what Lorentz's had in mind: canceling matter contraction. That is why the symmetric equations below are preferable: x = g * x' – beta * t' x' = g * x + beta * t Please note that distances may be given in light second or in wavelength units as well (then x = 1 stands for one lambda unit). Similarly, the variables t and t' may be given in seconds (which is time) or in wave period (which is the wave phase) units as well (in this case, t = 1 indicates 2 pi). The second equation shown above is merely the "mirror" image of the first one. This amazing symmetry was the keystone of Poincare's Relativity Postulate (1904). Please bear in mind that this is not my discovery. It is a well established procedure. I did have to modify Lorentz's equations, though, because this appears the only way to really making Maxwell's equations becoming invariant. It should be emphasized that Lorentz spoke about a "mathematical artifice". He added: "Especially, the t' variables cannot be considered as the true time." Such an unconceivable space/time transformation was misleading and useless. One should rely on equations whose structure merely reflects matter behavior. The software available below is a flawless demonstration that it works. What's more, it is much simpler this way because matter really contracts in accordance with g * x. This was indeed Lorentz's hypothesis. Moreover, the first equation also indicates that any object whose position was x = 0 should undergo a translation motion to x' = beta after a one second delay. Such a translation is a well known fact since Galileo: x' = x + v * t x = x' – v * t x' = x – v * t x = x' + v * t The interesting point is that those x et x' variables may be swapped as well without any preference for a given frame of reference. Even the sign only may be exchanged if one prefers the other one. Thus, modifying Lorentz's equations the same way appears acceptable. But given the fact that fast moving matter contracts and that frequencies slow down, it becomes obvious that Galileo was wrong and that there must exist a preferred stationary frame of reference, the aether, which is Cartesian, not Galilean. Then both x and t variables should definitely stand for axial coordinate and phase for matter at rest with respect to the aether. Such magnitudes become absolute and finally, non-Euclidean geometry appears totally weird, useless, and irrelevant. Please, let's make it simple!
A flawless demonstration. Please download this program: ...and also the FreeBasic editor/compiler: http://www.freebasic.net/index.php/download The compiled program shows how a moving source may undergo four different Doppler effects according to four different frequency shifts. I used Woldemar Voigt's equations in order to show that Lorentz version (where k = 1 becomes useless) is preferable. Lorentz used it in order to explain the Michelson interferometer contraction. Actually, as explained above, I had to use the reversed version because Voigt's original goal was to correct (not to produce) the Doppler effect. A Doppler effect occurs in all cases. But surprisingly, Voigt's constant may be adjusted to obtain a frequency shift. The second choice (B) reproduces the normal Doppler effect, which does not involve any frequency shift. Michelson was not aware that a frequency shift may occur, but he was perfectly aware that the wave relative speed should be faster transversally according to Lorentz's shrinking factor g (this means that this "aberration" was Michelson's discovery, not Voigt's). The Michelson interferometer was developed on this basis. The third choice (C) rather shows Lorentz's version, where the constant k = 1 becomes useless. In this case, the emitter frequency slows down according to g. I made the screenshot below because I know that just a few people will carefully examine this program. Please note that this is indeed a program. The computer does verify the equation set shown above. Thus, the results are highly reliable! |
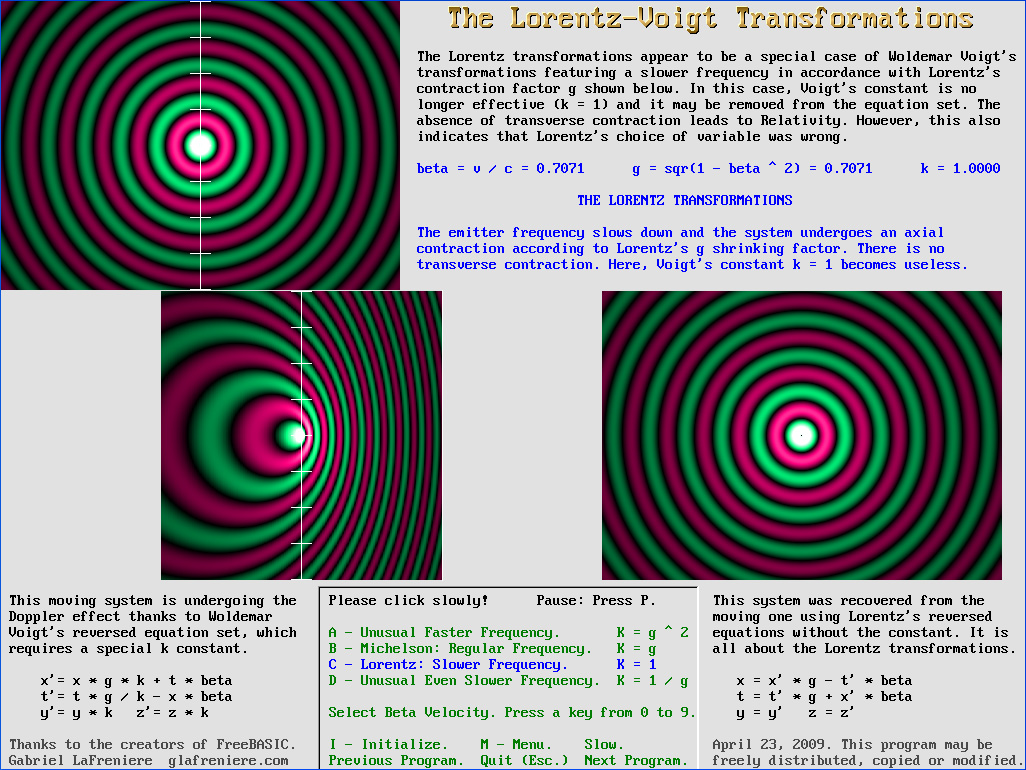
This is a screenshot from WaveMechanics06.bas
This program strongly suggests that the Lorentz transformations should have been formulated as follows:
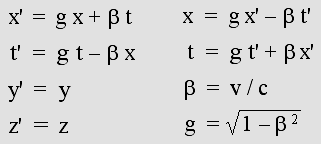
|
Poincare's misleading ideas. This program should persuade everybody that finally, the Lorentz transformations just modify matter coordinates and the wave period for a given coordinate. This produces an unusual Doppler effect whose main characteristic is a slower frequency. In this case, there is no transverse wavelength contraction any more, hence no transverse matter contraction either because matter exhibits wave properties. This is the very first condition for Maxwell's equations to becoming invariant so that Relativity becomes explainable. But unfortunately, instead of admitting that matter just transforms the same way standing waves do (this was discovered later by Yuri Yvanov), Poincare and Einstein strongly deviated from Lorentz's initial hypothesis. Their incredible ignorance of standing waves appears to be the chief explanation of their failure. They thought that optical phenomena were purely relative. Then the speed difference only is to be considered and consequently there is no preferred frame of reference any more. Especially, the aether must be ruled out as a material support for "electromagnetic waves" because it would obviously be a preferred frame of reference. One must rely on non-Euclidean geometry in order to manage those totally absurd ideas, and this finally ended with Minkowski's "space-time" even more absurd concept. This unbelievable story needs some more analysis. 1. Lorentz's initial idea was that the Michelson Interferometer had to undergo an axial contraction but no transverse transformation in order to explain Michelson's well known null result. This is possible only on condition that the wave period slows down and for this reason, one observes that clocks tick slower and do not indicate the same time along the displacement axis. I admit that all this is a bit puzzling, but I still must say here that I am rather surprised that nobody seems to have thoroughly examined this hypothesis. Even Lorentz himself did not. Amazingly, nobody elaborated a comprehensive Theory or Relativity on this basis, despite the fact that it was highly consistent. 2. I can easily read Poincare's books because I am French. It clearly appears that he just ruled out Lorentz's contraction without any further analysis (Electricity and Optics, 1901). He even stated that Lorentz's hypothesis did not yield satisfying results without any acceptable argument. Such properties for matter indeed appeared "strange" in 1901 (but much less today because we know that matter and especially electrons obviously exhibit wave properties), but they did explain Michelson's null result and many other unexplained phenomena such as Bradley's aberration of light. Thus, it had (and it is still) to be carefully examined. 3. The puzzling "local time" was discovered independently by Lorentz and Poincare. It should be pointed out that this phenomenon becomes undetectable only on condition that the contraction really occurs. It is quite worrying to remember that here, Poincare had a major advantage on Lorentz. He had been appointed to the "Bureau des Longitudes" in 1893 and he had to examine such "local hours", a mere consequence of the Earth's motion through the well-accepted aether. However, I could find no evidence that he did examine this phenomenon in the case of an hypothetic contraction. Apparently, he did not notice that in this case, the local time would become unnoticeable and surely, he did not admit that this was a major argument in favor of Lorentz's hypothesis. 4. A wave period may be useful for making amazingly precise clocks, but it is still not the "time". When Lorentz released his famous equation set using Voigt's t and t' variables, he did not realize that they were quite misleading. Displaying spherical waves on a large area must be performed in two different steps. Firstly, the distance to the emitter and its frequency must be taken into account. The precise wave period for a given coordinate is to be calculated according to the delay for each wave front to reach this coordinate. This delay must be given in absolute time units (do not try to introduce a time transformation here, it doesn't work!) and this is indeed all about time. However, the above computer program indicates that the Voigt-Lorentz equations do not account for this first procedure. They just rule the second step establishing the new emitter coordinates (because of the contraction) and its new phase (because of the slower frequency and also Michelson's apparently unequal wave speed). The point is: this phase is repetitive and it must be given in 2 pi units. To say it shortly, one must realize this it is not exactly what the concept of time is. The time has no true existence. It only refers to an arbitrary convention. In spite of this, Poincare introduced a "time dilation" concept and frankly, this is a shame. 5. In spite of his exceptional knowledge in physics, Poincare was definitely a mathematician and a philosopher well before being a physicist. That is why he was not especially interested in how the light mechanically propagates (it is still a mystery nowadays). He instantly agreed with Maxwell about those fast moving electric and magnetic fields which did not need an aether any more. His point was: "The equations work, why bothering about the mechanics?" And so, as soon as he could establish his own symmetric equation set, where there is no variable for the speed of light any more, Poincare immediately thought that the aether hypothesis could be abandoned. Once again, this is a shame. No true physicist would dare to rule out any plausible hypothesis unless he is fully aware of the nature of a physical phenomenon. 6. Poincare had abandoned the idea of absolute space and time units well before 1905. This quote is from his 1905 book (Science and Hypothesis): "All those things do not exist prior to the mechanics than the French language exists prior to all truths which are expressed in French". This is ridiculous. Relativity holds true because the moving observer is fooled by an unexpected and amazing Doppler effect. There is no other way to remain logical. For instance, he is unable to detect the aether wind by means of an interferometer because of matter contraction. Let's make things perfectly clear: facts are absolute, they simply cannot be relative. From this point of view, space and time units (as a convention) are also absolute. Thus, the time as proposed by the Greenwich observatory is arbitrary and somewhat unstable, but it is still absolute. Whatever his speed and position, any observer is capable of dealing with that on condition that he is well aware of the Lorentz transformations. 7. Euclid realized that evidences cannot be explained and he proposed some of them as "postulates". Evidences just need to become spontaneously present in one's mind but apparently, very few people are capable of this most unexplainable process: understanding. Admitting the quite obvious fact that the Earth is overpopulated is a good example... Although they remain disputable, Euclid needed postulates for elaborating his famous geometry, which still yields correct results today. However, in the last period up to his death, Poincare was interested in non-Euclidean geometry, which is a pure absurdity. This was his worst error. He was also interested in gravity, and as usual Einstein "borrowed" his ideas (the Mercury precession problem especially was firstly analyzed by Poincare). He developed a "General Relativity" theory based on space curvature. Let's put it this way: all this is totally absurd. It becomes clear that the main person responsible for leading us in a blind alley was Henri Poincare, who was shamelessly copied by Albert Einstein afterwards. We are now facing a lot of errors which prove to be an obstacle to further discoveries. Scientists working on GPS systems had to make their way out of Einstein's illogic postulates. Today, they are realizing that clocks and frequencies, and even the speed of light on Earth are a good absolute reference after all. The satellite clocks and the radio oscillators are known to tick a bit slower and they need to be adjusted in order to match those on Earth. If they are not, the radio waves emitted by the satellite are undergoing Lorentz's slower Doppler effect. This is measurable and verifiable on Earth, yet an astronaut in this satellite is totally unable to detect it. He is rather detecting a Doppler effect in the waves emitted from the Earth surface. And finally, the satellite contraction ratio is so tiny that it is still not detectable using our most accurate devices. But it does contract, and this behavior is detectable using much longer distances. Lorentz was a true physicist. That is why we had to trust Lorentz. Not Poincare or Einstein.
March 2009. Mr. Philippe Delmotte and Jocelyn Marcotte invented a wave medium algorithm many years ago. Then we worked hard to obtain the best results from it. Recently, a lot of annoying artifacts and anomalies were corrected. Now, our images are quite smooth and natural. The Michelson Interferometer. Below are several new improved video clips showing how light travels in the Michelson Interferometer. There is a choice of two velocities. Firstly, half of the speed of light or 0.5 c, and secondly, 0.7 c. Transverse waves are tilted to an angle which is given by: arc sin (v/c), that is 30° and 45°. This behavior proves to be highly consistent with the Lorentz Transformations. The interferometer contraction leads to a modified angle for the beam splitter, whose normal angle is 45° when the apparatus is stationary. Surprisingly, the new angle works fine and apparently, all seems to happen as though the interferometer was still at rest. Judge by yourself. Michelson_Interferometer.5c.mkv Michelson_Interferometer.7c.mkv Spherical outgoing waves are reflected on a parabola in order to obtain transverse plane waves. They are tilted to a theta = arc sin (v/c) angle. Thus, they are traveling slightly frontward in such a way that the interferometer constantly follows them. Then the beam splitter produces two separate and orthogonal beams which are reflected back by the plane mirrors. The mirror on the right is nearer to the beam splitter than the upper one because of the contraction, and the beam reunification indicates that Lorentz's hypothesis (Larmor and FitzGerald also proposed it) was correct. These images are also showing a very interesting optical effect: the beams are finally reunified by the beam splitter. Almost no light returns to the emitter. This occurs because the beam splitter does not really "reflect" the light beam. Matter on the transparent layer emits wavelets instead, whose phase is opposite. These wavelets cancel one half of the wave energy passing through it but their addition on a 90° angle produces a new wave front whose phase is lambda/4 shifted. This phenomenon is a confirmation that the light waves cannot be stopped by matter. Surprisingly, the shade behind matter is caused by wavelets whose phase is opposite. This is not really a surprise because radio waves, X-rays and gamma rays are not stopped by matter. Let's face it, most of the spectrum obeys this rule and the light is the exception. In addition, a metallic screen or wire (especially a parasite antenna) are well known to capture some of the energy and then emit such wavelets whose phase is opposite. According to their number and their distribution, they also produce a shade exhibiting a characteristic diffraction pattern. However, in this case, the beam splitter very thin reflecting layer is insufficient to cancel the whole energy passing through it. Naturally, one should compare with what is going on when the interferometer is really at rest. Michelson_Interferometer_Stationary.mkv It
is even more important to compare with what happens if the set does
not undergo Lorentz's contraction. The video below shows that
Michelson's calculus was correct - except for the contraction, which
was quite unpredictable. This proves that Lorentz's idea was just
great! Michelson_Interferometer_No_Contraction.mkv The codec is Mpeg-4 DivX 7 - DivX Plus (well established H-264/AAC) using Matroska files with .mkv extension. Matryoshka means "Russian dolls", as this system allows one to include a menu and many chapters, audio and subtitle choices, which could be useful here. Those files are significantly smaller for a given quality. I hope that the whole Internet will finally focus on them to get rid of all this mess about compatibility. Most of new DVD et Blu-ray players should easily play them, as well as Windows Media Player, Zoom Player, VLC Media Player, DivX Player, etc. If you still experience some difficulties, you may download (free, Zoom Player included) the whole nine yards from CCCP, which means Combined Community Codec Pack, not USSR! I wrote and used the FreeBasic program below to produce the diagrams: Decisive results. By comparison, Special Relativity now appears frankly unreasonable. Those results are actually devastating for supporters of Einstein's Special Relativity. They were comfortably installed in their unexplainable certitude but those new facts (and more to come) are definitely waiting for new explanations. Up to now, nobody seems to have clearly described this remarkable behavior. The good idea should be to reasonably explain the resulting appearance of Relativity without Einstein's absurdities. As a matter of fact, Lorentzian Relativity is still to elaborate. Lorentz was definitely on the right track but he never went beyond a mere explanation of Bradley's and Michelson's unexpected results and, perhaps, a better description of the transformed particles. What's worse, Henri Poincaré and Einstein ruled out matter contraction and (almost) the aether itself. Fortunately, they were all quite sure that faster then light speeds were impossible. This is not what some supporters of Lorentz's Relativity wrongfully think. Bradley's aberration of light. I also experimented successfully the Bradley aberration of light in a moving frame of reference. Then the emitted light waves are undergoing the Doppler effect. Once again, the results are perfectly compatible with the existence of the aether. The hard to detect aether wind was the main problem well before Michelson. Sir Airy, the famous astronomer, was strangely clinging to Fresnel's idea that the wind speed should be proportional to the refraction index for glass or water. His experience using a telescope filled up with water was still a failure. All those phenomena including Michelson's experiment and Bradley's aberration of light seemed totally unexplainable. Considering the complexity of those phenomena and the lack of tools to check them, the 1900's mess is quite understandable. But I finally obtained flawless proofs that a moving observer always sees his environment as though he were perfectly stationary. Thanks to the virtual medium and my Time Scanner, I can easily demonstrate that apparently, all optical phenomena don't change in spite of the Doppler effect, through a now fully acceptable aether. And once again, it is on condition that the emitter frequency really slows down and that Lorentz's contraction (especially that of an optical device such as a parabola) takes place only along the direction of motion. Those clips are especially revealing. They clearly show how curved waves undergoing the Doppler effect are reflected on a parabola. They are transformed into plane waves, but they become tilted to the theta angle = arc sin (v/c). Then they are reflected on a plane mirror in such a way that the interference pattern follows the phase wave, whose speed is 1/beta. All along this phase wave, Lorentz's t' "local time" does not change. Finally, the waves return to the parabola, which focuses them into a classical Airy Disk, albeit it is contracted and submitted to the same local time according to the phase wave. It turns out that Lorentz was right. It is a fact. It is undisputable... Bradley_Aberration_Plain.5c.mkv Bradley_Aberration_Plain_Stationary.mkv The program is here : Bradley_Aberration_Plain.5c.bas The frequency must slow down in order to cancel the transverse wavelength contraction along orthogonal axes y and z. Below, my goal was to show how parallax is still possible in the presence of motion, in spite of the Doppler effect. As a matter of fact, parallax was Bradley's original idea. Opticians know very well that off-axis images obtained by means of a parabolic mirror suffer from coma and astigmatism. They also suffer from spherical aberration if the object distance is finite. In spite of this, parallax detection is still possible. And once again, the parabola must contract to do this accurately. This even includes the distance between two of them! Bradley_Aberration_Parallax.5c.mkv Bradley_Aberration_Parallax_Stationary.mkv Program: Bradley_Aberration_Parallax.bas This movie clip especially shows that the two focuses occur at different "local times", which are given by the phase wave and by Lorentz's time equation. Relativity is not the point. We need a practical theory in order to obtain more correct results. We especially have to deal with GPS satellites whose results could be even more accurate. Because the Doppler effect is definitely involved, the Lorentz Transformations cannot be neglected any more. The Doppler effect is present, it is easily measurable, and according to those new results the parabola must contract in order to reflect microwaves correctly. Here, speaking about space and time transformation is totally useless. It is rather a matter of true contraction and slower clocks. After all, only our measures on Earth are to be preferred; in this particular case we do not have to bother about local space and time. The satellite clocks must definitely indicate Standard Time, not their own slower time. One should avoid synchronizing them using radio signals transmitted from one to another because we know that this procedure ends up with a time shift. It is not a matter of Relativity, it is just a mechanical problem which can easily be solved thanks to the Lorentz transformations. Surely, our Earth is not perfectly stationary with respect to the aether. However, one must firstly examine how those phenomena should occur if it was the case. The observer orbiting in a satellite is fully aware of his abnormal situation. Because he knows that his speed simply cannot be zero, he must admit that his emitter is sending waves which are undergoing the Doppler effect. He also knows that this effect is easily detectable on Earth, which is postulated to be stationary. And so, because is is still unable to detect the Doppler effect, his only remaining option is to reasonably explain why. The best way to do that is by means of this fantastic virtual medium which I used to make the video clips available in this page. Scientists working on the GPS system are aware that C compilers are now very fast on a Pentium processor and that today's graphic cards work great. Large arrays of computers working in parallel and even supercomputers are available. Thus, one can experiment those effects in a fast, accurate and effective manner in a very large virtual medium. It is a genuine laboratory despite the fact that it handles virtual waves. Explaining Relativity. About Lorentz's contraction effects, Henri Poincare wrote (Electricity and Optics, 1901) : "This strange property would truly seem a "helpful hand" from Nature to hide from our eyes the absolute motion of the Earth in spite of optical phenomena. This cannot satisfy me..." Well, he was wrong. This "strange property" seems indeed a miracle (not to say a conspiracy considering the additional time shift and, thirdly, those slower clocks). It seemed so unlikely that this could occur that Lorentz finally abandoned his original hypothesis, which was still the only reasonable one. But today, thanks to this new virtual medium, and also to my Time Scanner, it becomes obvious that the orbiting observer is unable to detect his motion. Firstly, the phase wave cancels the Doppler effect. And later, the same phase wave cancels the time shift. Surprisingly, both focal planes appear simultaneous and perfectly symmetrical during a given t' time. This happens because waves traveling backward are faster, so that the information only appears simultaneous. In addition, because he himself is contracted, the observer cannot detect the remaining contraction either. Now, we can explain why the observer is fooled. Bradley_Aberration_Parallax_Scan.mkv Program: Bradley_Aberration_Parallax_Scan.bas Seeing this, one must admit that the relative speed of light is slower forward than backward. The difference seems to cancel the Doppler effect, but there is still a Doppler effect. From this point of view, the Earth being the preferred frame of reference, the speed difference only, not the absolute speed, should be considered. It becomes clear that optical phenomena and even mechanical phenomena still appear identical in the satellite environment. Even length contraction is unnoticeable because the observer is also contracted. This is why the observer orbiting in the satellite is fooled. We found the cause. Now, let's examine the Bradley aberration of light. Bradley's goal was to measure the distance to the nearest stars by detecting a parallax effect. The Earth's orbit proved to be a bit too small to do this, but Bradley unexpectedly discovered a different phenomenon. Because the speed of the Earth around the Sun is about 29 km/s, the telescope motion produces a small but measurable focus offset. Bradley soon realized that this effect was a consequence of the speed of light. Our virtual medium can easily show this. It is quite impossible to set the emitter (which represents a star) several light years away, but a large parabola produces the equivalent plane waves. Then let's add two small parabolas (Bradley's telescope) moving in opposite directions the way they would do around the Sun at 6-month intervals. In this first experience, the Sun is postulated to be perfectly stationary and the telescope speed is exaggerated to 1/3 of the speed of light in order to obtain a more dramatic effect. Bradley_Aberration_Stationary.mkv Program: Bradley_Aberration_Stationary.bas No surprise here: the Airy disk pattern reaches the point where the parabola optical axis was previously. This result is quite simple and understandable. It was a good idea to firstly show what is normally going on, though, because the two parabolas and the wave patterns no longer remain symmetric if the Sun is moving. Today, we know very well that the Sun is orbiting around the galaxy center even faster then the Earth does around the Sun. The point is: Bradley did obtain a perfect symmetry. Such a result seemed to indicate that the sun is perfectly stationary with respect to the aether. Surely, the sun motion should rather introduce a severe asymmetry. Here, let's suppose that the Sun is moving at about one half of the speed of light. When both the Sun and the Earth are moving in the same direction, the speed of the Earth is accelerated to .5 + .33 = .83 c. Otherwise, it is rather slowed down to .5 - .33 = .23 c. So the Earth and the parabolas must periodically contract in accordance with Lorentz's shrinking factor. However, in order to reproduce the same 1/3 c velocity as above, as seen by the moving observer, one must refer to Poincare's law of speed addition, which is given by: beta'' = (beta + beta') / (1 + beta * beta') It turns out that the slowest and fastest composite speed should be .2 and .7143 c. Then the contraction difference is severe: 98% vs. 70%. Obtaining a symmetric result using those differently contracted parabolas now appears unlikely to be possible, especially in the presence of the additional Doppler effect. Poincare's 1901 theory ("optical phenomena are relative") was attractive because it was much simpler and apparently correct. I am quite sure that Lorentz did figure out such a scenario because Bradley and Michelson had severely damaged Newton's system. He had to abandon his hypothesis, for he was a great scientist. It simply could not work. Program: Bradley_Aberration.5c.bas But surprisingly, the video below shows that it does work! Using my Time Scanner, which transforms a Doppler distorted environment the way a moving observer should see it, it becomes obvious that a perfect symmetry is still possible. Bradley_Aberration.5c_Scan.mkv Program: Bradley_Aberration.5c_Scan.bas This is certainly the most amazing phenomenon ever. I did not doubt that when I initiated the video series because I know a lot about the Lorentz transformations and the Doppler effect. Writing so complicated programs was not a piece of cake, but I finally succeeded in showing that Lorentz's theory definitely works great! Lorentz's triumph is now complete. No doubt, this is the ultimate experiment. In the future, it will be repeated and improved to a high degree of perfection, and it will always yield the same fantastic results. Lorentzian Relativity. This leads to Lorentz's Relativity. Consequently, Special Relativity is deadly wounded. Einstein's version (actually that of Poincare) was indeed attractive because it yielded correct predictions. No doubt, it was valuable, but now we need to know why all this is possible. We need to know how matter works. The basic principle is that any moving system still mechanically works perfectly on condition that those strange effects take place. Because of them, the moving observer cannot be aware of his motion any more. He still see things in his environment as though he were perfectly at rest. So it was important to elaborate the correct equation set for this, as Lorentz's purpose was rather to cancel the Doppler effect on Maxwell's equations in a moving frame of reference. Surprisingly, Lorentz's x' and t' variables applied to the stationary system. This is weird. Knowing this, I just swapped them and easily obtained the equation set below many years ago:
The Lorentz Transformations. This modified set is fully consistent with Lorentz's point of view.
Let's make things perfectly clear: Lorentzian Relativity simply cannot be explained without those equations. They must be adopted by any scientist who is interested in Lorentz's works, even though Lorentz neglected to put them down this way. Secondly, I demonstrated a long time ago that those equations also produce Lorentz's slower Doppler effect. In this case, x variables stand for axial distances in wavelengths and t variables stand for the wave period, hence in 2*pi units. And thirdly, this is highly consistent with my Time Scanner. Three independent and spectacular confirmations of the same facts cannot be a coincidence. The Lorentz Transformations are definitely a law of nature, and they are all about matter mechanics. Clearly, they will lead us well beyond Relativity. Fortunately, in this form, Lorentz's equations become quite easy to understand. One must bear in mind that all x and x' variables stand for absolute distances in light seconds, so that c = 1. On the contrary, while only t variables stand for absolute seconds, Lorentz carefully explained that t' variables do not indicate the "true time". They only indicate slower seconds that clocks in this moving frame of reference should display. Suppose that velocity is 50% of the speed of light, hence beta = 0.5 and Lorentz's contraction factor is: g = 0.866. And finally, x = 1 and a one second delay (t = 1) occurred. 1. g * x means that matter and distances contract to 86.6% of their original length along the direction of motion in accordance with Lorentz's contraction factor. 2. beta * t means that matter simply moves to x' = 0.5 * 1 = 0.5 light second after a one second delay according to its speed. This is Galileo's Relativity Principle. However, because the coordinate was shifted to x'=0.866 after the contraction occurred, the final x' position is 0.866+0.5= 1.366 light second. 3. g * t means that moving clocks tick 86.6% slower, once again according to Lorentz's contraction factor. More exactly, the electron frequency and that of any cyclic mechanical process slows down. This is why the transverse wavelength, hence transverse distances, remains constant according to Lorentz's y'=y; z'=z. 4. –beta * x means that a clock whose original position was x = 1 (but whose position is currently x' =1.366 light second) indicates minus 0.5 second as compared to another clock whose original position was x = 0 (but whose position is currently x' =0.5 light second). This time shift is important because, in this frame of reference, the relative speed of light is three times faster backward (1+beta=1.5) than forward (1–beta=0.5). As a consequence, and additionally because the contraction is unnoticeable as well, the clock synchronization procedure using light or radio signals perfectly matches this anomaly. It should be emphasized that this is not only a mere time shift. Cause and effect relationships are undergoing the same Doppler distortion, simply because causes are transmitted by waves. Thus, speaking about space and time transformation is meaningless and useless. One should rather consider that this appearance of simultaneity leads to an amazing but understandable mystification: the moving observer cannot detect his true speed through the aether any more. This time shift can also be cross-checked by means of the phase wave, where Lorentz's t' time remains the same. It is where transverse waves incoming from opposite directions encounter, given the fact that they are tilted to an angle which is given by: arc sin (v/c). The result is a scissor effect. Because of this constant but "moving" t' time, two observers A and B placed on the displacement axis will think that the wave front crosses this axis at the same time. So it will seem parallel to it, not tilted. I invented my Time Scanner thanks to this phenomenon. The phase wave is well visible in the Bradley_Aberration_Parallax.5c.mkv clip above. At all events, I made another video clip in order to show this in a more dramatic manner. It shows how waves behave in a moving confocal and symmetric twin-parabola system, which is a very rarely shown optical or radio apparatus. Here, the phase wave is visible two times, firstly for plane but tilted waves, then for moving circular standing waves (please observe that they look very much like my moving electron, but in 2-D only). FreeBasic program: Phase_Wave.bas Poincare's Relativity Postulate. So, let's return to the very beginning of this story. In 1904, Henri Poincaré made a lecture to the International Congress of Arts and Science in St-Louis, Missouri, USA. No doubt that Albert Einstein was well aware of what he said: "The laws of physical phenomena must be the same, whether for an observer fixed, or for an observer carried along in a uniform movement of translation, so that we have not or cannot have any means of discerning whether or not we are carried along in such a motion."
This site is very popular and it becomes more and more discussed. Thanks to my efforts, things are about to change. A lot of new sites whose subject is "Lorentzian Relativity" (check Google) are available. This is quite a revolution. Thus, if one still prefers to rely on Einstein's weird principles and paradoxes, making all those new results still compatible with his version of the theory will soon become unsustainable. I admit that Einstein's predictions are correct (clearly, Relativity is true), but his interpretation of what is really going on is not.
Gabriel LaFreniere |
Home page: Matter is made of waves.
Notice. webmaster@glafreniere.com
|
A Fantastic Wave Simulator! Mr. Philippe Delmotte invented his amazing wave algorithm in June 2005. He finally released the English version in May 2009: In the near future, those wave simulators will become a must for opticians and acousticians. It is indeed a powerful laboratory allowing one to observe and study all wave phenomena. I am quite sure that it will especially become unavoidable for studying matter waves. It is a well known fact that matter exhibits wave properties. In spite of that, up to now, very few people realized that matter waves cannot be just an analogy. Waves are waves. Here, one is dealing with standing waves, wave fronts, amplitude, frequency, wavelength, interference patterns, etc. The goal is to show that regular waves can influence spherical standing waves. Thus, considering that the electron is a pulsating wave center, two of them put together are surely capable of influencing one another. This is all about Newton's action and reaction law. You may uncompress the file in any directory. Click the image, then click the "New Project" icon on the upper left corner to clear the wave area. Click the concentric wave icon to obtain a pulsating wave center. You may change its position, amplitude, wavelength, etc. You may also add a second one to observe interferences. There is also a linear emitter (observe the Fresnel-Fraunhofer diffraction), a circular emitter (producing circular standing waves in the center), a parabola, etc. This is much more interesting than flavorless equations. I made a lot of similar programs and I succeeded in showing that waves are surprisingly unpredictable. Their "personality" is mainly dependent on the medium properties. That is why we need to explore many wave algorithms. However, I already made my choice: in order to achieve the electron amplification, the aether should be made of granules repelling themselves. In my picture, it must be compressible. |